|
ALUMINUM POTASSIUM SULFATE
| ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 7784-24-9 (Decahydrate) 10043-67-1 (Anhydrous) |
|
| EINECS NO. | 233-141-3 | |
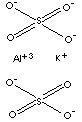
| FORMULA |
AlK(SO4)2·12H2O | |
| MOL WT. | 474.37 | |
|
H.S.CODE |
||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | Kalinite; Potash alum; Potassium alum dodecahydrate; | |
| Alum; white alum; Aluminiumkaliumbis(sulfat) (German); Bis(sulfato) de aluminio y potasio (Spanish); Bis(sulfate) d'aluminium et de potassium (French); Sulfuric acid, aluminium potassium salt (2:1:1); | ||
| SMILES |
aluminium hydroxide with potassium sulfate in sulfuric acid |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
white crystals or powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 92 - 93 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 200 C (Decomposes) | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.757 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | very soluble | |
| pH | 3 - 3.5 (10% solution) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | 16.4 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT | Not combustible | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
|
The term of alum refers to various isomorphous solid sulfates composed of trivalent metals and univalent metals, especially aluminum potassium sulfate, AlK(SO4)2·12H2O, a white, crystalline compound. Alums have the general formula M2SO4·MIII2(SO4)3·24H2O, where M is one of alkali metals (potassium, sodium, rubidium, caesium, silver. thallium or ammonium), and MIII denotes one of the trivalent cation (e.g., aluminum, chromium, iron, manganese, cobalt, or titanium). In aqueous solution, alums show all the chemical properties that their components show separately. These salts are used in water purification, leather tanning, coagulation agent for rubber latex, setting dyes (mordant), fireproofing textiles, modifying concrete, baking powder, preparation of lakes, clarifying of turbid liquids and as astringents.
Flocculants are used in water
treatment. The addition of flocculants to raw water causes colloids
and other suspended particles to stick together and form heavier particles (floc) which will be
removed by the sedimentation or filterability. This flocculation
(or called coagulation) process is to aid the removal of
contaminants like fine solid pollutants or microscopic molecules which are
difficult or
impossible to be removed by filtration alone. Generally flocculants are multivalent cations such as aluminium, iron,
calcium or magnesium. Many of the suspended water particles have a negative electrical charge
which repels each other. Positively charged flocculants attract and stick to many of the suspended water particles.
Many of flocculant s cations, under appropriate pH and other conditions, react with water to form insoluble hydroxides which
join together to form larger settleable particles or
physically traps
small particles into the larger floc. There are organic flocculants also. The
most common and powerful organic flocculant is polyacrylamide
which have the long-chain to trap
small particles into the larger floc. One of the common coagulants is aluminum sulfate
which ,under neutral or slightly-alkaline conditions,
reacts with water
to form gelatinous precipitate of aluminum hydroxide. Polyaluminum chloride
(PAC) of the general formula AlnCl(3n-m)(OH)m
is useful as this compound have a wide range of pH value
according to the subscripts
n and m.
The actual pH correlates to the formula m/(3n).
It provides a choice for
the exact pH
value applications. The most common PAC for water
purification is Al12Cl12(OH)24.
The
form of Al2Cl(OH)5
is
used as a deodorant and an
antiperspirant. Other modified PAC compouinds include
polyaluminum hydroxidechloride silicate (PACS) and polyaluminum hydroxidechloride
silicate sulfate (PASS). Members of flocculants include:
|
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystals or powder | |
|
CONTENT |
99.5% min (on dry basis) | |
| Fe | 0.02% max | |
| Pb | 0.02% max | |
|
WATER INSOLUBLES |
0.01% max | |
|
PARTICLE SIZE |
1 - 2mm | |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
43.0 - 46.0% | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25 kg, 1mts in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. |
| |
| OTHER
INFORMATION
|
||
|
|
||